Injection molding is one of the most common manufacturing processes used today. From car parts and electronics cases to toys and medical devices, injection molded plastic parts are everywhere.
But what exactly is injection molding and how does it work? In this comprehensive guide, as a professional plastic injection molding manufacturer, I’ll walk you through the injection molding process step-by-step. I’ll also share actionable tips to help you get the most out of this versatile manufacturing technique.
An Overview of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique for producing plastic parts in large volumes. It works by injecting molten plastic material at high pressure into a mold cavity. The plastic cools and hardens into the shape of the mold, allowing for the mass production of intricate, highly accurate plastic parts.
So in a nutshell, here are the key steps of injection molding:
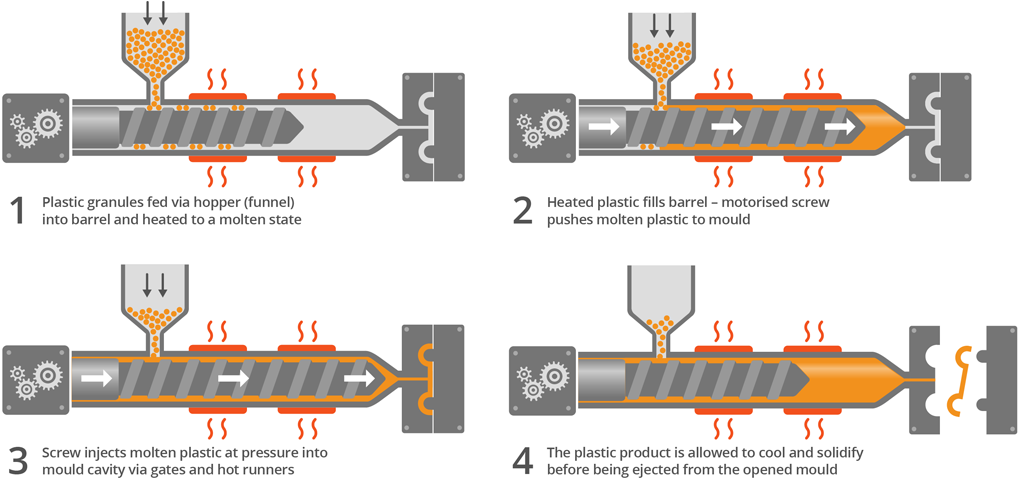
- Plastic pellets are fed into the injection molding machine through a hopper
- The pellets are heated, melted, and turned into a liquid inside the machine’s barrel
- The melted plastic is injected through a nozzle into the mold cavity at high pressure
- It’s held under pressure as it fills the entirety of the mold
- The plastic part is cooled and solidified
- The mold opens and the finished plastic part is ejected
This full cycle then repeats, allowing for continuous production runs of plastic injection molded parts.
Now let’s break down each of these injection molding process steps in more detail.
What is the Process of Injection Molding?
Step 1: Feeding in the Plastic Pellets
The plastic that gets injection molded starts off in pellet form. These small cylindrical pellets, usually made of thermoplastic material, are poured from a hopper into the injection molding machine’s barrel.
Common thermoplastics used include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). However, the versatility of injection molding allows for many types of plastic to be used.
Step 2: Heating and Melting
Next, the plastic pellets move forward inside the barrel as they’re heated by steel heaters surrounding it. A rotating screw continuously mixes the pellets to promote even melting.
Most thermoplastics melt between 150°C and 370°C. Maintaining the optimal melt temperature is crucial so that the plastic fully liquefies without burning inside the barrel. The result is a completely molten plastic ready for injection.
Step 3. Injecting Into the Mold Under High Pressure
The mix of molten plastic then gets injected through a gate and into the mold cavity. The injection nozzle presses the plastic into the mold with intense pressure, typically between 10 and 15,000 PSI.
This high pressure packs the material tightly into every crevice of the mold cavity, ensuring no air gaps exist. Molds are precisely machined metal blocks that can withstand these immense pressures.
Step 4: Holding Under Continued Pressure
To make sure no shrinkage occurs before the plastic part sets, pressure is continually applied as the mold cavity fills. The pressure gets held steady for an extended “dwell time”, usually a few seconds.
This dwelling phase gives the material time to completely pack into the extremities of the mold before it starts to cool.
Step 5: Cooling and Solidifying
As the injected materialdwells, cooling channels surrounding the mold start to reduce the temperature inside. This cooling period allows the plastic part to solidify whilst maintaining its molded shape.
Once sufficiently cooled after a few minutes, the rigid plastic part inside is ready for removal from the mold. Cooling times depend on the size and complexity of the injection molded part as well as the plastic type used.
Step 6: Opening the Mold and Ejecting the Plastic Part
Finally, the mold separates and opens up, typically in a clamshell style fashion. Ejector pins push the finished injection molded plastic part out of the mold where it gets picked up by an operator or a robotic arm.
Sprues and runners — the channels that delivered the material into the cavity — get removed from the solid plastic part, which then heads down the production line for finishing. This full sequence then repeats as quickly as every 30 seconds, allowing for high-volume plastic part production.
And there you have the full injection molding process! Each step is critical for producing accurate, high-quality injection molded components out of plastic. Tweaking any variable can directly impact the properties and precision of the end product.
But when optimized correctly, injection molding delivers unbeatable manufacturing efficiency and produces intricate plastic parts affordably even in vast quantities. This makes it an essential industrial process suitable for everything from prototyping to full-scale production.
Key Takeaways: How Injection Molding Works
To quickly recap, here are the key things to know about the injection molding process:
- Plastic pellets get fed into a barrel
- Heat melts the pellets into a liquid state
- The molten plastic gets injected into a metal mold under extreme pressures
- It dwells and fills the mold completely before cooling
- The plastic part gets solidified before the mold opens
- Ejector pins remove the finished plastic component
Understanding the injection molding process allows you to produce custom plastic parts at scale. So if you’re ready to explore this versatile manufacturing method for your next project, get in touch with our engineering team who can walk you through the entire injection molding workflow from design to final parts.
