Das Kunststoffspritzgießen ist heute eines der gängigsten und vielseitigsten Herstellungsverfahren. Von Spielzeug und Haushaltswaren bis hin zu medizinischen Geräten und Autoteilen - spritzgegossene Kunststoffteile sind überall zu finden.
Wenn man bedenkt, wie allgegenwärtig und nützlich das Spritzgießen von Kunststoffen ist, stellt sich natürlich die Frage: Gibt es ein gleichwertiges Verfahren für Metallteile? Wie sich herausstellt, gibt es ein Metallgussverfahren, das dem Kunststoffspritzguss sehr ähnlich ist: das Druckgussverfahren.
In dieser Stelle, als Fachmann Hersteller von Kunststoff-SpritzgussteilenIn diesem Kapitel werden wir einen detaillierten Blick darauf werfen, wie Druckguss im Vergleich zum Spritzguss abschneidet, um zu sehen, warum er als die Metallversion dieser beliebten Fertigungstechnik angesehen werden kann.
Welches Metallgussverfahren ist dem Kunststoffspritzguss am ähnlichsten?
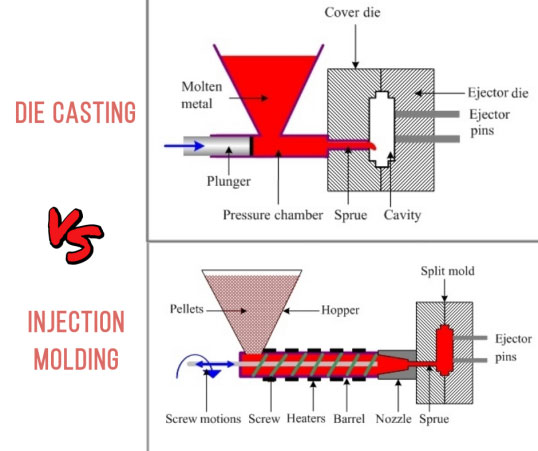
Das Metallgussverfahren, das dem Kunststoffspritzguss am ähnlichsten ist, ist der Druckguss. Beim Druckguss wird eine geschmolzene Metalllegierung unter hohem Druck in Stahlformen eingespritzt, wodurch komplexe Metallteile mit hohen Toleranzen in Serie hergestellt werden können. Dies spiegelt mehrere Schlüsselphasen und -fähigkeiten des Spritzgussverfahrens wider und qualifiziert den Druckguss als das nächstliegende Metalläquivalent.
Wie das Kunststoffspritzgießen funktioniert
Bevor wir einen Vergleich mit dem Druckguss anstellen können, sollten wir uns kurz ansehen, wie das herkömmliche Spritzgießen funktioniert. Hier ist der Standard-Spritzgießprozess:
Das Kunststoff-Rohmaterial wird im Inneren des Zylinders der Spritzgießmaschine geschmolzen. Zu den häufig verwendeten Kunststoffen gehören ABSPVC, Nylon, HDPE und Polycarbonat. Der Kunststoff wird durch Hitze und Druck von einer rotierenden Schnecke geschmolzen.
Der nun flüssige Kunststoff wird in eine Stahlform gespritzt. Die Form ist geschlossen und wird durch Wasserleitungen geschmiert und gekühlt. Der Kunststoff füllt den Hohlraum und nimmt die Form der Form an.
Das geformte Teil kühlt in der Form ab bis sie fest genug sind, um ausgeworfen zu werden. Die Abkühlzeiten hängen vom verwendeten Kunststoff und der Wandstärke ab, liegen aber in der Regel zwischen 20 Sekunden und 2 Minuten.
Die Form öffnet sich, und das fertige Kunststoffteil wird ausgeworfen. Ein geringfügiges Beschneiden der Teile ist erforderlich, um überschüssigen Kunststoff und Formlinien zu entfernen.
Dieses schnelle 4-stufige Verfahren ermöglicht die Massenproduktion komplizierter Kunststoffteile mit Präzision, Effizienz und Wiederholbarkeit. Aber gibt es ein Äquivalent aus Metall?
Druckguss im Vergleich zum Spritzgießen
Druckguss ist ein Herstellungsverfahren, bei dem geschmolzenes Metall unter hohem Druck in eine Stahlform, die sogenannte Kokille, gespritzt wird. Die gängigsten Druckgussmetalle sind Nichteisenlegierungen aus Zink, Aluminium, Magnesium und Kupfer.
Dies mag bereits sehr ähnlich klingen wie das Kunststoffspritzgießen, aber sehen wir uns die einzelnen Phasen einmal genauer an:
Vorbereitung der Form
Dieser Schritt ist bei beiden Verfahren nahezu identisch. Die Metallmatrizen oder Stahlspritzgussformen werden mit einem Schmiermittel besprüht und dann verschlossen. Dies hilft bei der Temperaturkontrolle und dem Auswerfen der Teile.
Füllen der Form
An dieser Stelle werden die Ähnlichkeiten deutlich. Beim Druckguss wird das geschmolzene Metall durch einen Schwanenhals in die Gussform gespritzt. Druck, Temperatur und Geschwindigkeit werden sorgfältig kontrolliert, um den Formhohlraum zu füllen.
Genau wie beim Spritzgießen können mit dem Druckgussverfahren dünne, komplexe Metallteile mit hoher Toleranz hergestellt werden.
Abkühlung und Erstarrung
Nach dem Füllen der Form beginnt das geschmolzene Metall schnell abzukühlen und zu erstarren, wobei es die Form der Metallform annimmt. Die Abkühlungszeiten hängen von der verwendeten Legierung und der Wandstärke ab, sind aber in der Regel kürzer als beim Kunststoffspritzgießen.
Teil-Auswurf
Schließlich trennt sich die Matrize, und das erstarrte Metallteil wird ausgeworfen. Es werden auch einige kleinere Entgratungsarbeiten durchgeführt, um überschüssiges Metall und Grat zu entfernen.
Wie Sie aus diesem Vergleich ersehen können, funktioniert das Druckgießen ähnlich wie das Kunststoffspritzgießen, nur mit geschmolzenem Metall anstelle von Kunststoff. Dies qualifiziert es als das gleichwertigste Metallherstellungsverfahren.
Einzigartige Vorteile des Druckgusses
Abgesehen von den Verfahrensähnlichkeiten bietet das Druckgießen einige einzigartige Vorteile, ähnlich wie das Spritzgießen von Kunststoffen:
- Fähigkeit zur Herstellung komplexer, hochtoleranter Metallteile im Massenmaßstab
- Sehr schnelle Produktionszykluszeiten
- Niedrige Kosten pro Einheit bei höheren Stückzahlen
- Breite Werkstoffauswahl an gießbaren Legierungen
- Hoher Grad an Automatisierung möglich
Diese vorteilhaften Eigenschaften haben das Druckgießen zum bevorzugten Verfahren für die Herstellung von Metallteilen in vielen Industriezweigen gemacht, z. B. in der Automobilindustrie, der Luft- und Raumfahrt, der Elektronik und der Konsumgüterindustrie.
Mit Druckguss lassen sich haltbare Metallteile herstellen, die im Vergleich zu anderen Metallverarbeitungstechniken eine geringere Maßgenauigkeit aufweisen. Dies ermöglicht die Herstellung kleiner, aber komplizierter Metallteile in großem Maßstab, ähnlich wie beim Spritzgießen von Kunststoffen.
Hauptunterschiede zwischen Druckguss und Spritzguss
Obwohl das Druckgussverfahren viele Gemeinsamkeiten mit dem Kunststoffspritzguss aufweist, gibt es auch einige bemerkenswerte Unterschiede:
Verwendete Materialien: Der Hauptunterschied besteht darin, dass beim Spritzgießen Kunststoffpolymere verwendet werden, während beim Druckgießen ausschließlich geschmolzene Metalllegierungen zum Einsatz kommen. Jedes Verfahren ist auf die jeweilige Materialart zugeschnitten.
Schimmelkosten: Aufgrund der hohen Temperaturen und Drücke sind Druckgussformen komplexer und teurer als Kunststoffspritzgussformen. Allerdings halten sie in der Regel auch mehr als 1 Million Schuss.
Nachbearbeiten: Druckgussteile erfordern nur wenig Nachbearbeitung, da sie mit glatten Oberflächen ausgeworfen werden. Spritzgegossene Kunststoffe müssen in der Regel entgratet, strukturiert oder dekoriert werden.
Vorlaufzeit: Druckguss hat im Allgemeinen schnellere Zykluszeiten als Spritzguss, insbesondere bei kleinen, dünnwandigen Teilen. Das Prototyping im Kunststoffspritzguss ist jedoch mit kostengünstigeren Aluminiumformen einfacher.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass die beiden Hauptunterschiede in den verwendeten Materialien und der Komplexität/Kosten der Form liegen. Der eigentliche Herstellungsprozess ist ansonsten recht ähnlich.
Welches Verfahren ist das richtige für Ihre Anwendung?
Wir haben viel über den Vergleich zwischen Druckguss und Kunststoffspritzguss gesprochen. Lassen Sie uns die wichtigsten Erkenntnisse zusammenfassen:
- Das Druckgießen funktioniert ähnlich wie das Spritzgießen, jedoch mit geschmolzenem Metall anstelle von Kunststoffpolymeren.
- Beide können komplexe, hochtolerante Teile in Massenproduktion herstellen
- Druckguss bietet einzigartige Vorteile wie Festigkeit, Hitzebeständigkeit und schnellere Zyklen
- Kunststoff-Spritzgießen bietet niedrigere Kosten und Materialflexibilität
Welche ist also für Ihr spezielles Produkt oder Ihre Anwendung sinnvoll?
Hier sind einige Leitlinien:
Kunststoff-Spritzgießen funktioniert in der Regel besser, wenn Sie es brauchen:
- Niedrige Stückkosten, insbesondere bei sehr hohen Stückzahlen
- Leichte Teile mit Korrosionsbeständigkeit
- Geringe Anlauf- und Prototyping-Kosten
- Kreative Freiheit bei Farben, Texturen und Materialien
Druckgießen funktioniert in der Regel besser, wenn Sie dies wünschen:
- Hochfeste und hitzebeständige/abriebfeste Metallteile
- Komplizierte Bauteile mit sehr engen Toleranzen
- Glattere Oberflächen, die nicht nachbearbeitet werden müssen
- Schnelle Produktionszykluszeiten
Für manche Anwendungen können beide oder sogar eine Kombination sinnvoll sein. Aber die Bewertung Ihrer spezifischen Anforderungen und Prioritäten wird Ihnen bei der Auswahl des besten Verfahrens helfen.
Die Vielseitigkeit des Kunststoffspritzgießens hat es zum bevorzugten Herstellungsverfahren für die Massenproduktion von Kunststoffteilen in unzähligen Branchen gemacht. Der Druckguss bietet dieselbe Fähigkeit, Effizienz und Präzision, allerdings für kostengünstige Metallteile.
Wenn Sie also schon immer über ein Metallherstellungsverfahren nachgedacht haben, das ähnliche Vorteile wie das Spritzgießen bietet, dann sind Sie beim Druckguss genau richtig - er kommt einer Metallversion dieser allgegenwärtigen Produktionstechnik am nächsten.
