Le moulage par injection repose sur l'utilisation de la bonne quantité de plastique fondu, ou "taille de la grenaille", pour remplir complètement la cavité du moule. Le coussin fait référence à la capacité supplémentaire de la grenaille au-delà de ce qui est nécessaire pour remplir le moule. Ce coussin de plastique a pour fonction essentielle de maintenir la pression sur le matériau qui se refroidit et se rétrécit dans le moule pendant la phase de remplissage du cycle de moulage par injection.
Comprendre les coussins permet aux mouleurs d'optimiser la qualité, les tolérances et l'uniformité des pièces. Poursuivez votre lecture, en tant que professionnel fabricant de moulage par injection de matières plastiquesJe vais vous présenter ce concept essentiel du moulage par injection.
L'importance des coussins dans le moulage par injection
Le maintien de la pression pendant l'emballage est essentiel à la bonne formation des pièces. Lorsque le plastique chaud s'écoule dans un moule relativement plus froid, il commence à perdre de la chaleur au profit des parois du moule. Le plastique qui se refroidit rétrécit également en volume. Sans une pression adéquate, le matériau s'éloignerait des surfaces du moule, ce qui réduirait la précision et la qualité des pièces.
Le coussin constitue un réservoir de plastique fondu qui continue d'exercer une pression sur le matériau de durcissement. Cette pression entraîne du plastique supplémentaire dans les zones de rétraction afin de maintenir le contact avec le moule. Une pression de remplissage adéquate est nécessaire pour produire des pièces complètes et précises sur le plan dimensionnel.
Prévention des défauts de pièces
Un amortissement inadéquat peut être la cause directe de défauts courants sur les pièces, tels que les coups courts, les marques d'enfoncement et les pièces déformées. Lorsque la pression de garnissage diminue prématurément, le retrait du matériau forme des défauts visibles. Le maintien de la pression de tassement pendant la durée requise permet de garantir que les pièces sont complètes et conformes aux spécifications.
Fonctionnement des coussins dans le moulage par injection
Maintenant que vous savez pourquoi les coussins sont importants, voyons comment cette capacité de production supplémentaire permet d'améliorer la qualité des pièces :
L'unité d'injection
Les machines de moulage par injection modernes utilisent une vis à l'intérieur d'un cylindre chauffé pour faire fondre des granulés de plastique. En tournant, la vis fait avancer la matière en fusion à travers un clapet anti-retour. L'accumulation de plastique fondu devant l'extrémité de la vis s'appelle la grenaille.
Remplir le moule
Pour le processus d'injection, la vis se déplace vers l'avant, agissant comme un piston pour forcer la grenaille à travers la buse, la carotte, les canaux et dans les cavités du moule. La course de la vis détermine la taille de la grenaille.
Emballage de la pièce
Après avoir rempli le moule, le plastique fondu continue de s'écouler pendant la phase de remplissage. Il exerce une pression sur le matériau de refroidissement, qui se rétrécit à l'intérieur du moule.
Le maintien de cette pression est essentiel pour produire des pièces complètes et de bonne dimension. À mesure que le matériau perd de la chaleur et se rétrécit, la pression de tassement fait entrer du matériau supplémentaire pour compenser. Lorsque la pression du plastique est égale à celle du moule force de serragele portail se fige, ce qui met fin à la phase d'emballage.
Pourquoi le coussin est vital pour la pression d'emballage
Le démoulage nécessite une pression plastique sur le matériau de vulcanisation. Sans coussin entre la pointe de la vis et l'entrée du moule, il n'y aurait rien pour exercer cette pression essentielle pendant l'emballage.
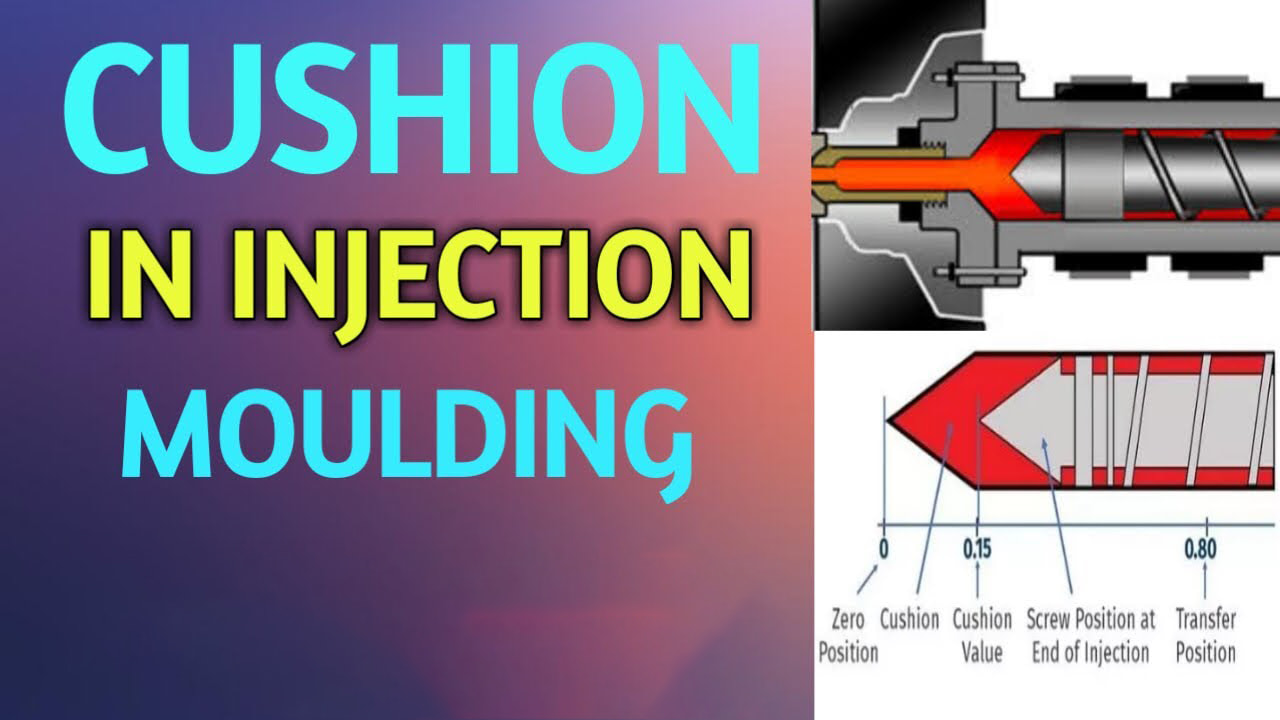
Coussin de mesure
Le coussin fait référence à la capacité d'injection restante entre la fin de la course d'injection et la course maximale de la vis. Il est généralement mesuré comme une distance linéaire entre la pointe de la vis et la buse à la fin du remplissage.
La distance typique entre les coussins pour une machine de taille standard est comprise entre 5 et 10 mm. Les unités d'injection plus grandes nécessitent des coussins plus grands. La taille optimale du coussin dépend du moule, du matériau, du taux de remplissage et d'autres facteurs.
Coussin de surveillance
Étant donné que le coussin détermine la pression de garnissage, le maintien d'un coussin constant d'un tir à l'autre est essentiel pour la constance de la pièce. La variation autorisée dépend des exigences de tolérance de la pièce.
La tolérance typique du coussin est de ±10%, ce qui offre une marge de manœuvre suffisante pour les variations de la machine tout en permettant des performances reproductibles. L'examen des données historiques aide les mouleurs à optimiser la variabilité admissible des coussins en fonction des exigences de capacité de chaque moule.
Comment augmenter l'amortissement dans le moulage par injection
Si votre coussin actuel est insuffisant, voici des méthodes éprouvées pour l'augmenter en toute sécurité :
1. Vérifier les paramètres du processus
Commencez par vous assurer que vos vitesses de transfert et d'injection ne sont pas trop élevées. Une vitesse excessive peut entraîner un "dépassement" prématuré des coussins disponibles.
Ensuite, réduisez votre pressions d'emballage et de maintien. L'utilisation de pressions plus faibles permet souvent d'augmenter l'accumulation de coussins.
Enfin, allonger légèrement les temps d'emballage. Cela donne une marge de manœuvre supplémentaire à la vis pour qu'elle progresse avant de se bloquer.
2. Augmenter la contre-pression
En augmentant la contre-pression, on s'oppose directement au mouvement de la vis, ce qui permet à la matière de s'accumuler. Commencez par une pression prudente et augmentez-la progressivement.
Une contre-pression trop importante risque de surchauffer/dégrader le polymère. Observer attentivement tout signe de modification indésirable des propriétés du matériau.
3. Vérifier la fermeture de la buse
Si les ouvertures des buses ne se ferment pas complètement entre les tirs, la matière en fusion peut s'écouler inutilement vers l'arrière.
Inspecter les anneaux de contrôle, les vis de réception et les buses de canaux chauds pour s'assurer de leur bonne étanchéité. Remplacer les composants usés si nécessaire.
4. Réduction des vitesses de remplissage
Un remplissage trop rapide du moule réduit la quantité de coussin qui s'établit dès le départ. Essayez de réduire les vitesses de remplissage par petits incréments jusqu'à ce que la valeur cible du coussin se stabilise.
Des vitesses de remplissage excessivement lentes peuvent également poser des problèmes. Veillez à ce que l'aspect des pièces reste acceptable lorsque vous réglez les vitesses de remplissage.
5. Vérifier l'absence de composants usés
Avec le temps, les barillets, les vis et les clapets anti-retour s'usent et perdent de leur consistance. Demandez à un technicien qualifié d'inspecter les principaux composants de l'outillage et de les remplacer si les tolérances se sont considérablement dégradées.
Si la réparation des pièces usées peut s'avérer coûteuse, le rétablissement de la santé de la machine de moulage par injection se traduit par une amélioration de la capacité du processus et une réduction des taux de rebut.
Choisir la bonne taille de coussin
Plusieurs facteurs déterminent la taille appropriée du coussin pour chaque moule :
- Taille de la machine - Les unités d'injection plus importantes nécessitent une plus grande distance de calage.
- Viscosité du matériau - Les matériaux à viscosité plus élevée nécessitent plus de coussin.
- Taux de remplissage - Un remplissage plus rapide exige plus de pression disponible.
- Taille de la pièce - Les pièces plus grandes nécessitent un temps d'emballage plus long.
- Exigences de tolérance - Des tolérances plus étroites nécessitent moins de variance.
C'est dans la fenêtre de fonctionnement de ces contraintes que se trouvent la taille optimale du coussin et la variabilité autorisée. Les capteurs de pression fournissent des données en temps réel sur la pression dans l'empreinte afin d'aider les mouleurs à définir les réglages optimaux du coussin.
Une fois établies, le respect constant de ces spécifications est essentiel pour obtenir des performances de moulage reproductibles. Une surveillance continue permet de corriger tout écart avant de produire des pièces défectueuses.
Trop ou pas assez de coussin peut causer des problèmes
Des coussins insuffisants exercent une pression de tassement inadéquate, tandis que des coussins surdimensionnés peuvent surcharger le matériau.
Les coussins surdimensionnés augmentent également les risques de pénétration de plastique dégradé dans la pièce. Trouver le bon équilibre permet d'éviter ces défauts. Les données historiques guident les mouleurs dans l'optimisation des coussins pour une performance stable.
À emporter
Le maintien de la pression d'emballage est essentiel pour produire des composants moulés par injection complets et de bonne qualité dimensionnelle. Cette dépendance de la pression de tassement souligne l'importance du coussin.
Le réglage du coussin permet aux mouleurs d'atteindre les densités d'emballage nécessaires pour chaque moule. Une fois définie, la surveillance continue du coussin est impérative pour permettre une production constante de pièces de bonne qualité.
La compréhension des coussins met en lumière cet élément vital qui sépare la fabrication de composants de haute performance de la production de déchets.
