Injection molding is one of the most common manufacturing processes for creating plastic parts and products at scale. Understanding shot size – the amount of molten plastic injected into the mold cavity with each cycle – is key for efficiency and quality. But what exactly is shot size, and why does it matter so much in injection molding? As a professional plastic injection molding manufacturer, I will help you find it out.
What Is Shot Size in Injection Molding?
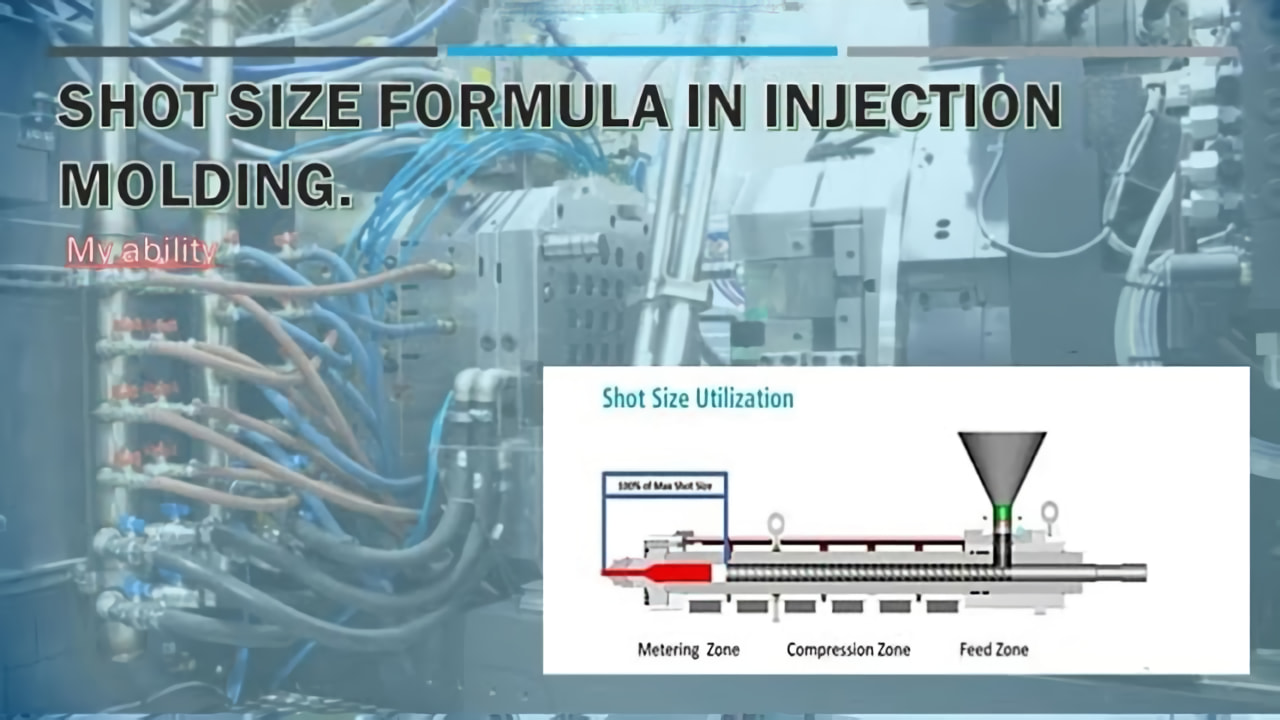
The shot size refers to the volume or weight of molten plastic that fills the injection mold tool during each injection molding cycle. It is the amount of material that is injected through the nozzle into the mold cavity to create the desired plastic part.
The shot size capacity of an injection molding machine is the maximum volume or weight of material that can be injected by the screw into the mold per shot. Shot capacity is determined by factors like the machine’s screw diameter and maximum stroke length.
Why Is Shot Size Important in Injection Molding?
Dialing in the optimal shot size for your specific mold tool and material is crucial for several reasons:
Part Quality
Using the right shot size helps ensure complete cavity fillout, uniform melt fronts, minimal voids/short shots, and overall high part quality. Overpacking can cause issues like sinks and warpage.
Cycle Efficiency
The proper shot size allows for fast injection without requiring excess cooling time, optimizing cycle times. Oversized shots prolong cooling.
Dimensional Consistency
Consistent shot sizes shot-to-shot allows for uniform shrinkage and tight dimensional tolerances.
Material Waste
An efficient shot size minimizes the amount of excess material wasted in sprues/runners. Oversized shots increase waste.
How Is Shot Size Calculated for Injection Molding?
Determining the optimal shot size requires information about the:
- Part geometry: dimensions, volume, projected surface area
- Material: type, density, flow properties
- Mold: runner and gate design, number of cavities
- Machine: injection pressure capacity, screw size
With this data, proper shot sizes can be calculated with formulas accounting for material densities, cavity volumes, runner weights, gate dimensions, and processing factors like packing percentages.
Computerized mold filling simulations are also commonly used today to analyze cavity fillout and optimize shot sizes.
Shot Size Estimation Rules of Thumb
As a starting point, injection molding engineers often use rules of thumb to estimate shot sizes:
- Shot weight = 1.1–1.3 x part + runner weight
- Shot size = 10–20% over part volume
- Shot size = 25–65% of maximum shot capacity
These are then fine-tuned through mold trials and adjustments.
How Does Shot Size Affect Injection Molding Part Quality?
Molders must strike a delicate balance with shot sizes. Problems arise on both ends of the spectrum:
Short Shots
If the shot size is too small, the mold cavity will not fill completely, creating short shot parts with voids. Common causes are low injection pressures, inadequate shot capacities, or obstruction in runners.
Flash
Conversely, a shot size exceeding the optimum amount can lead to flash – excess material leaking from the mold seam lines. Typical causes are overpacking high injection pressures.
What Happens If Shot Size Is Too Large or Small?
Both undersized and oversized shot sizes can negatively impact the injection molding process and quality:
Too Small Shot Size Issues
- Short shots/incomplete fill
- Voids in parts
- Weak weld lines
- Dimensional variance
Too Large Shot Size Problems
- Longer cycle times
- Sink marks
- Warpage
- Flash
- Increased material waste
Dialing in the “Goldilocks” shot size – not too much, not too little – is imperative for injection molding success.
Conclusion
The shot size, representing the amount of plastic injected into the mold with each cycle, is a make-or-break parameter that must be optimized for every injection molding project. Careful shot size selection ensures molded part quality, efficiency, and consistency shot-to-shot. Both undershot and overshot sizes lead to defects. By accurately accounting for part geometries, materials, and other factors, molders can zero in on the ideal shot weight or volume to maximize process control and product quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is shot size specified?
Shot size can be specified by either volume (cubic centimeters or inches) or by weight (grams or ounces). In general, shot weight is more commonly used.
What affects the injection molding shot size?
Shot size is influenced by the size and geometry of the part, material being molded, density/flow rate of the material, runner and gating design, number of cavities, machine shot capacity, and processing parameters.
How much extra should the shot be versus part volume?
As a general rule of thumb, the shot size should be 10-20% greater than the total cavity volume in order to ensure proper packing and account for material shrinkage.
Can you change the shot size on an injection molding machine?
Yes, shot size can be adjusted on injection molders by changing the machine’s stroke length or screw position controls, within the limits of the machine’s shot capacity. Getting the shot size dialed in properly usually involves some trial and error testing.
