Injection molding is a common manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts. At the heart of every injection mold is the core and cavity which shape the final molded product. But what exactly are the core and cavity? And what is the difference between them?
In this comprehensive guide, as a professional plastic injection molding manufacturer, I will share everything you need to know about the core and cavity in injection molds including:
- Definitions of the core and cavity
- The differences between them
- Their importance in injection molding
- Factors that affect core and cavity design
- How to choose the optimal placement
Let’s dive in…
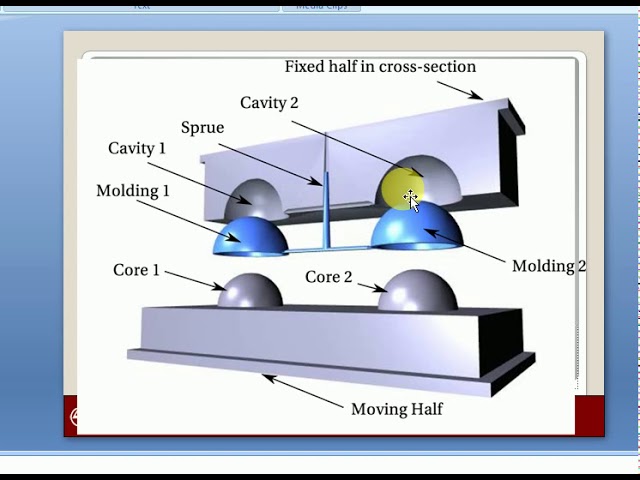
What is a Mold Core?
The core is the male portion of an injection mold. It’s typically made from machined steel or aluminum.
When the mold closes, the core forms the interior geometry of the final plastic part. This includes details like threads, ribs, bosses, and injection points.
Here’s a quick definition:
The core is the inner part of an injection mold that forms the interior contours and features of the molded component.
What is a Mold Cavity?
The cavity is the female portion of an injection mold and is also made from machined steel or aluminum. The cavity forms the exterior geometry of the final molded plastic component. This includes critical dimensions, parting lines, ejector pin marks, surface finish, and more.
In summary:
The cavity is the outer portion of an injection mold that forms the visible contours and exterior cosmetic features of the molded plastic part.
Key Differences Between the Core and Cavity
Now that you know the basics, let’s look at some of the key differences between the injection mold core vs cavity:
Location
- Core – Internal features
- Cavity – External features
Responsibilities
- Core – Structural integrity and function
- Cavity – Appearance and cosmetics
Importance in Injection Molding
Proper design of both the core AND cavity are critical to produce accurate, high-quality parts via injection molding. However, they play slightly different roles:
- The core ensures the molded part will meet functional requirements and specifications. This includes strength, durability, and performance metrics.
- The cavity is focused mainly on aesthetics. This includes parting lines, release draft, surface finish, flash control, and overall appearance.
Now let’s look at some reasons why the core and cavity are so vital in injection molds.
Why the Core and Cavity Are Important
The core and cavity account for up to 95% of the final injection molded part cost according to some estimates. This is because precision CNC machining is required to create the highly complex contours needed to produce plastic components.
Here are some of the reasons the core and cavity are integral components:
Dimensional Accuracy
The cavity and core form the final plastic part shape and control critical dimensions. Proper construction and machining ensures the tightest tolerances which lead to accuracy and consistency.
Appearance
While the cavity plays the biggest role in appearance, the contour of the core can also influence the exterior shape in subtle ways. Maintaining precision across both halves of the mold produces attractive, flawless parts.
Strength and Function
The core forms reinforcing ribs, bosses for inserts, and other strength-enhancing features. This imparts durability while controlling flex and preventing breakage.
Cycle Efficiency
Properly designing the cavity and core for optimal cooling channel placement shortens cycle times allowing for faster production rates.
Longevity
Precision-machined steel cores and cavities withstand millions of injection cycles without wear or degradation leading to maximum mold lifespan.
Let’s look closer at some factors that influence core and cavity design…
What Affects Core and Cavity Design?
While there are high-level differences between mold cores and cavities, keep in mind – the specifics of each injection mold are unique.
Here are some considerations that affect core and cavity placement and design:
Plastic Part Design
The specifics of the components being produced including size, geometry, wall thickness, strength requirements, and material selection influence manufacturability.
Draft Angles
Angling vertical surfaces in the mold allows parts to release cleanly without sticking. Draft angle requirements affect core and cavity complexity.
Ejection System
Ejector pins must push the cooled part out of the mold half containing the cavity. Core and cavity placement choices support proper part ejection.
Number of Cavities
When producing multiple plastic parts per molding shot, the configuration must allow for equal flow and uniform cooling.
As you can see, there are many interdependent variables requiring substantial expertise to create a robust, mass production-ready injection mold.
Next, let’s look at some best practices for choosing core and cavity placement…
How to Choose Core and Cavity Placement
While every injection mold requires unique consideration, here is some guidance regarding core and cavity placement:
Part Geometry
Complex parts with deep draws or other formed features should use a female cavity and male core arrangement. This helps control material flow and replication accuracy.
Wall Thickness
Areas of an injection molded component with thicker walls take longer to cool. These sections should be oriented closest to cooling channels to prevent defects.
Strength Requirements
Ribs and gussets meant for strengthening the plastic part should be formed using protruding details on the core. This prevents molded-in stresses.
Material Selection
Faster cooling, higher viscosity resins often use more detailed cavity side textures to hide weld/flow lines. Core side textures can lead to internal stresses in these materials.
Ejection Considerations
All parts must remain secured to the mold half containing ejector pins even as they shrink. Analysis using mold flow simulation software helps predict optimal core/cavity layouts.
Getting core and cavity placement perfect is challenging but pays major dividends in part quality and mold productivity.
Conclusion
The cavity and core form the entire geometry of injection molded components. Their precision machining and proper alignment are directly responsible for part accuracy, appearance, strength, and manufacturability.
While the cavity and core have slightly different focuses, both halves of the mold must be robustly constructed from durable materials and cleverly designed to withstand millions of cycles.
Careful analysis and planning of core and cavity placement while considering plastic resin behavior and characteristics leads to a mold with the highest performance and longevity.
Now you should have a complete understanding of what the mold core and cavity are, their subtle differences, why they’re vital in injection molding, and best practices for integrating them into your next project!
