Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts at scale. But what exactly is shot weight, and why does it matter when injection molding?
The shot weightis a crucial concept that directly impacts the quality and consistency of molded parts. In this comprehensive guide, as a professional plastic injection molding manufacturer, we’ll break down what shot weight is, why it’s important, and how to accurately calculate it. Let’s dive in.
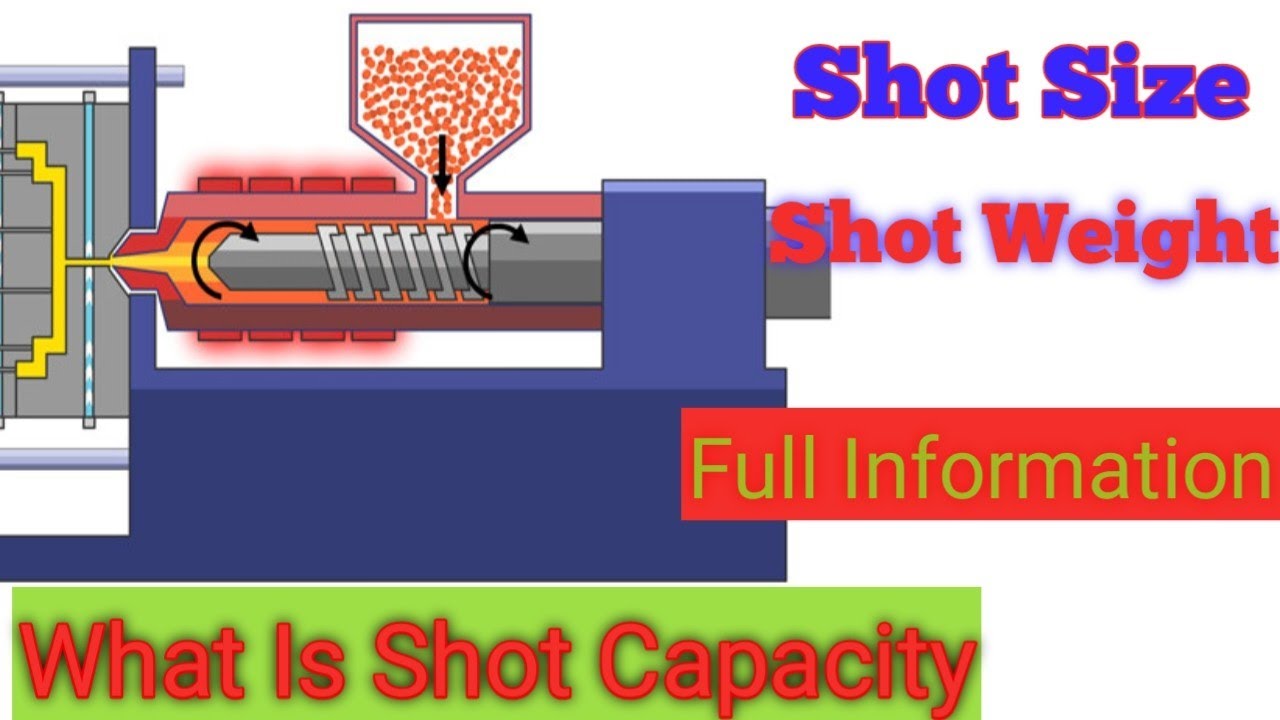
What Is Injection Molding Shot Weight?
Injection molding shot weight refers to the amount of material that gets injected into the mold cavity during each injection molding cycle.
It represents the total weight of the plastic resin or material required to fill the mold and produce the desired part. Shot weight is typically measured in grams (g) or ounces (oz).
For example, if 100 g of polyethylene is injected into the mold cavity in each shot, then the shot weight for that process is 100 g.
Shot Weight vs. Shot Size in Injection Molding
While related, shot weight and shot size have distinct meanings in injection molding:
Shot Weight – The weight of material injected to fill the mold per shot. Depends on part volume and material density.
Shot Size – The maximum volume the injection unit can inject per shot. Based on screw and barrel capacity.
Simply put, shot weight is an output while shot size is an input in the injection molding process. Properly matching shot weight to shot size is key.
Why Is Shot Weight Important in Injection Molding?
Dialing in the right injection molding shot weight is critical for:
- Part Quality – Insufficient shot weight → short shots/voids. Excessive shot weight → sinks, warpage, flash.
- Dimensional Accuracy – Shot weight impacts material flow/distribution in cavity.
- Material Use Efficiency – Optimized shot weight minimizes raw material waste.
- Cycle Time – Adjusting shot weight affects fill time and cooling rate.
- Cost Efficiency – Tight shot weight control = less scrap material and improved productivity.
In essence, accurate shot weight is vital for producing consistent, high-quality, dimensionally precise plastic parts via injection molding.
How to Calculate Injection Molding Shot Weight
Calculating injection molding shot weight involves:
Step 1: Determine Part Weight
The target weight of the finished plastic part. Provided in design specs or calculated via part geometry and material density.
Step 2: Identify Material Density
Unique density of plastic resin being used, typically in g/cm3 or lb/in3. Check resin supplier data.
Step 3: Calculate Part Volume
Volume = Length x Width x Height. Can use CAD models.
Step 4: Identify Mold Cavity Volume
Total volume of all cavities in mold. Consider multi-cavity molds.
Step 5: Factor in Material Yield
Account for runners, gates, scrap – typically 70-90% yield.
Step 6: Factor in Shrinkage
How much part shrinks as it cools – check resin shrink rate.
Step 7: Consider Packing Efficiency
Extra material to minimize voids – varies, estimate via trials.
Step 8: Apply Conversion Factor
Convert volume to weight using material density value.
With those parameters nailed down, the general injection molding shot weight formula is:
Shot Weight = (Part Volume + Runner Volume) x Material Density x (1 + Shrinkage Rate) x Packing Efficiency
Seems complicated, but most factors are provided or can be easily calculated. Let’s walk through an example shot weight calculation.
Injection Molding Shot Weight Calculation Example
Let’s say we want to determine the shot weight to mold a plastic electronics enclosure part with the following specs:
- Part Dimensions = 4 x 6 x 1 in
- Part Material = ABS (density of 1.05 g/cm3)
- Runner System Volume = 20 cm3
- ABS Shrink Rate = 0.5%
- Assumed Packing Efficiency = 1.05
First, calculate the part volume:
Length x Width x Height = 4 in x 6 in x 1 in = 24 in3 (394 cm3)
Then, factor in the runner system volume and material factors:
Shot Weight = (Part Volume + Runner Volume) x Density x (1 + Shrink Rate) x Packing Efficiency
Plugging in our values:
Shot Weight = (394 cm3 + 20 cm3) x 1.05 g/cm3 x (1 + 0.005) x 1.05
Performing the math, the shot weight equals 435 g
This is the target amount of ABS to inject into the mold in order to produce a quality, void-free enclosure part. Dialing in the proper shot weight setting on the injection molding machine will be essential.
Hot Runner vs Cold Runner Shot Weights
There’s an important distinction regarding shot weights for hot runner vs cold runner mold systems:
Hot Runner Shot Weight
Only includes material to fill mold cavities since hot runners remain molten between shots.
Cold Runner Shot Weight
Must account for runner system material since it solidifies after each shot.
Thus cold runners increase the calculated shot weight compared to hot runners.
Conclusion
Determining the optimal injection molding shot weight is vital for replicating parts within tight tolerances, maximizing manufacturing efficiency and ensuring product quality.
If you have any further questions about shot weight in injection molding, feel free to comment below.
